Introduction
Computers have become an integral part of our daily lives, revolutionizing the way we work, communicate, and access information. Throughout history, computers have evolved significantly, from the early vacuum tube-powered behemoths to the cutting-edge artificial intelligence-driven machines of today. This article explores the fascinating journey of computer generations, each representing a significant leap in technology and capabilities.
What is a Generation of Computers?
A generation of computers refers to a phase in the development of computer technology marked by fundamental changes in hardware, architecture, and capabilities. Each generation represents a major step forward in terms of processing power, size, efficiency, and versatility.
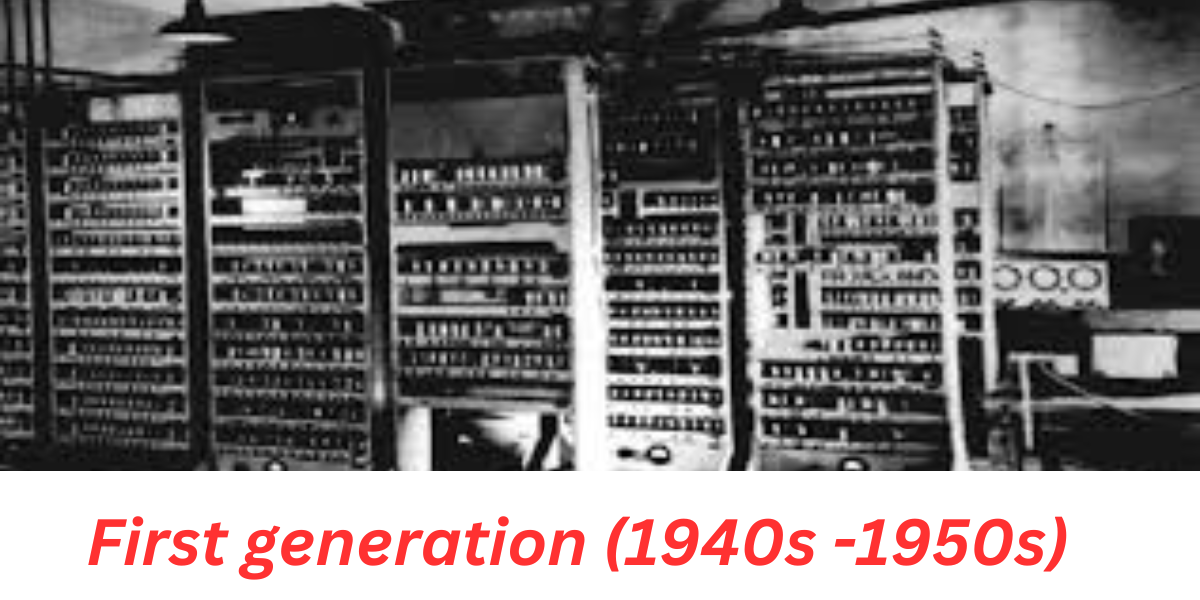
. First Generation Computers (1940s – 1950s)
The first generation of computers emerged in the 1940s and lasted until the 1950s. These early computers relied on vacuum tubes as their primary components for processing data. The use of vacuum tubes posed significant challenges, as they were large, generated a considerable amount of heat, and were prone to frequent failures.
Vacuum Tubes
Vacuum tubes were glass or metal tubes that controlled the flow of electrons to perform basic calculations. Although they were revolutionary at the time, they were highly unreliable and limited the overall speed and efficiency of the computers.
ENIAC and UNIVAC
One of the most prominent computers of the first generation was the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC). It was massive, occupying an entire room, and was primarily used for military calculations during World War II. Later, the Universal Automatic Computer (UNIVAC) became the first commercially available computer and marked a significant milestone in computer history.
. Second Generation Computers (1950s – 1960s)
The second generation of computers emerged in the 1950s and continued until the 1960s. During this era, vacuum tubes were replaced by transistors, bringing significant improvements in reliability and processing speed.

Transistors
Transistors were smaller, more reliable, and generated less heat compared to vacuum tubes. They allowed computers to become smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient.
IBM 1401 and IBM 7090
The International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) played a crucial role in the development of second-generation computers. The IBM 1401 was a popular business computer, while the IBM 7090 was known for its scientific and engineering capabilities.
. Third Generation Computers (1960s – 1970s)
The third generation of computers spanned from the 1960s to the 1970s. It brought about a significant advancement in computer technology with the invention of integrated circuits.

Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits combined multiple transistors and other electronic components onto a single semiconductor chip. This breakthrough drastically reduced the size of computers while improving their performance and efficiency.
DEC PDP-11 and IBM System/360
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) introduced the PDP-11 series, which became one of the most popular minicomputers during this period. Additionally, IBM released the System/360, a family of mainframe computers that set new industry standards.
. Fourth Generation Computers (1970s – 1980s)
The fourth generation of computers emerged in the 1970s and extended into the 1980s. It was characterized by the development of microprocessors, which brought computing power to the masses.

Microprocessors
Microprocessors integrated the central processing unit (CPU) on a single chip. This innovation led to the creation of personal computers (PCs) and revolutionized the way people interacted with technology.
Apple II and IBM PC
The Apple II, released by Apple Inc., became one of the first successful personal computers, gaining popularity for its user-friendly design and graphical interface. The IBM Personal Computer (PC) further popularized personal computing and became a standard in the industry.
. Fifth Generation Computers (1980s – Present)
The fifth generation of computers emerged in the 1980s and continues to the present day. This generation is marked by the development of artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced parallel processing.

Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is a field of computer science that aims to create machines capable of mimicking human intelligence. AI technologies have enabled computers to perform complex tasks such as natural language processing, image recognition, and decision-making.
Cray-1 and IBM Watson
The Cray-1 supercomputer, developed by Cray Research, showcased the power of parallel processing and was used in various scientific and engineering applications. IBM Watson, a breakthrough in AI, demonstrated its capabilities by defeating human champions on the quiz show “Jeopardy!”
. Sixth Generation Computers (Future Possibilities)
The sixth generation of computers represents the potential future developments in computing technology. While not fully realized yet, two promising avenues are quantum computing and DNA computing.
Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations at an exponentially faster rate than classical computers. It holds the promise of solving complex problems currently beyond the reach of traditional computing.
DNA Computing
DNA Computing explores the possibility of using DNA, the molecule that carries genetic information, to perform computations. This area of research is still in its infancy but shows immense potential for ultra-efficient computing.
The Impact of Computer Generations on Society
Each generation of computers has had a profound impact on society and various industries. The rapid advancements in computing technology have transformed the world in numerous ways.Computer generations have significantly shaped society.
First-generation computers in the 1940s laid the foundation for computation, revolutionizing industries like science and defense.
Second-generation computers in the 1950s introduced transistors, improving speed and reliability.
Third-generation computers in the 1960s facilitated commercial applications, altering business practices.
Fourth-generation computers in the 1970s brought microprocessors, fueling the personal computing era. Each generation has advanced technology, fostering societal progress and transforming the way we live, work, and communicate.
Advancements in Science and Medicine
Computers have revolutionized scientific research and medical discoveries. They enable complex simulations, data analysis, and genetic research that accelerate progress in these fields.
Automation and Efficiency in Industries
Computers have automated processes in industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and finance. Automation has improved efficiency, reduced errors, and optimized resource utilization.
Communication and the Internet
The internet, a product of advanced computing, has revolutionized communication and information access worldwide. It has transformed the way we communicate, learn, and conduct business.
Challenges and Concerns of Computer Generations
While computer generations have brought immense benefits, they also present unique challenges and concerns.
Privacy and Security Issues
As computers become more interconnected, data privacy and security have become major concerns. The risk of data breaches and cyberattacks demands robust cybersecurity measures.
Environmental Impact
The increasing use of computers and electronic devices contributes to electronic waste and energy consumption. Sustainable practices must be adopted to minimize the environmental impact.
Conclusion
The evolution of computers generations showcases humanity’s relentless pursuit of technological advancements. From the early vacuum tube-powered computers to the potential of quantum and DNA computing, each generation has pushed the boundaries of what is possible. These advancements have transformed our lives, society, and industries, leading us towards an exciting future powered by cutting-edge technologies.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What is the first generation of computers? The first generation of computers emerged in the 1940s and 1950s, relying on vacuum tubes for processing.
- What is the latest generation of computers? The latest generation is the fifth generation, characterized by artificial intelligence and parallel processing.
- What is quantum computing? Quantum computing is a revolutionary computing paradigm that leverages quantum mechanics for exponentially faster computations.
- How do computers impact scientific research? Computers enable complex simulations, data analysis, and genetic research, accelerating scientific advancements.
- What are the concerns of computer generations? Concerns include data privacy, cybersecurity, electronic waste, and energy consumption.